Semester
Subject
Year
B.Sc Computer Science and Information Technology
Institute of Science and Technology, TU
Design and Analysis of Algorithms (CSC325)
Year Asked: 2079, syllabus wise question
Backtracking
1.
What do you mean by Backtracking? Explain the backtracking algorithm for solving knapsack problem and find the solution for the problem given below and capacity of knapsack is 10 kg
[10]
Divide and Conquer Algorithms
1.
Explain the divide and conquer strategy for problem solving. Describe the worst-case linear time selection algorithm and analyze its complexity. [10]
2.
Trace the quick sort algorithm for sorting the array and write its best and worst complexity. [5]
Dynamic Programming
1.
Write the dynamic programming algorithm for matrix chain multiplication. Find the optimal parenthesization for the matrix chain product with size of each is given as . [10]
2.
Find the edit distance between the string "ARTIFICIAL" and "NATURAL" Using dynamic programming. [5]
Foundation of Algorithm Analysis
1.
Write short notes on: a) Best, Worst and average case complexity b) Greedy Strategy [5]
2.
Solve the following recurrence relations using masters method.
[5]
Greedy Algorithms
1.
Find the MST from following graph using Kruskal's algorithm. 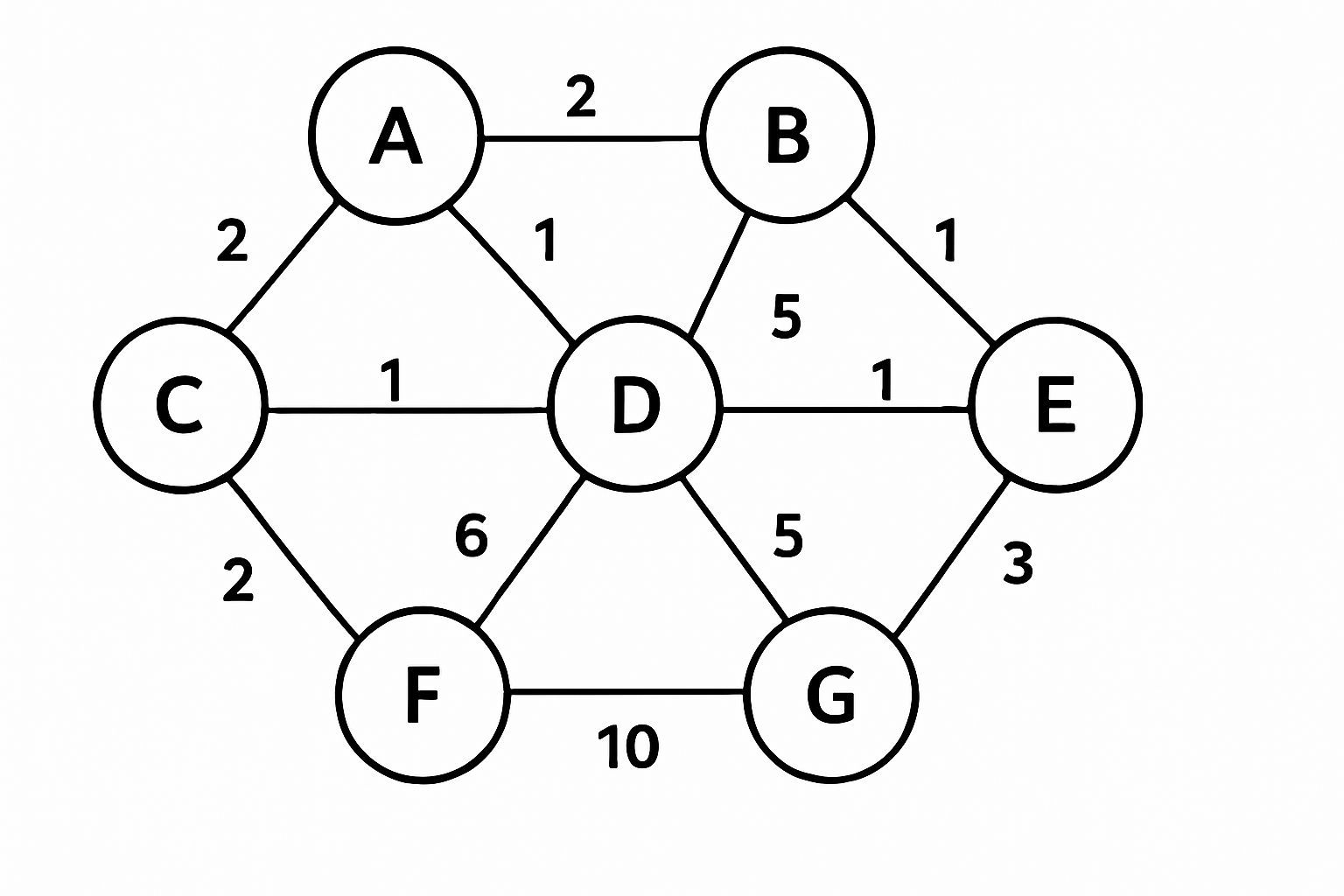 [5]
[5]

Iterative Algorithms
1.
Explain the iterative algorithm to find the GCD of given two numbers and analyze its complexity. [5]
NP Completeness
1.
Define tractable and intractable problem. Illustrate vertex cover problem with an example. [5]
Number Theoretic Algorithms
1.
Generate the prefix code for the string "CYBER CRIME" using Huffman algorithm and find the total number of bits required. [5]
2.
Solve the following linear congruences using Chinese Remainder Theorem. [5]