Semester
Subject
Year
B.Sc Computer Science and Information Technology
Institute of Science and Technology, TU
Theory of Computation (CSC262)
Year Asked: 2081, syllabus wise question
Basic Foundations
1.
Does machine always refer to hardware? Justify. Define positive closure and Kleene closure. [5]
2.
Define -closure of a state. Differentiate between Moore and Mealy machine. [5]
Context Free Grammar
1.
Define the language of a grammar. For the grammar , show the leftmost derivation for the string 00100 with its parse tree.
[5]
2.
Convert the following grammar to CNF.
[5]
Introduction to Finite Automata
1.
Design the DFA that accepts binary string ending with '00' and show its extended transition function for the string 111000. [5]
Push Down Automata
1.
Mention the transition function of PDA. List the two ways that PDA accepts the string. Convert the following CFG to PDA.
[10]
Regular Expressions
1.
List any two regular operators. Minimize the following finite state machine using Table Filling algorithm. 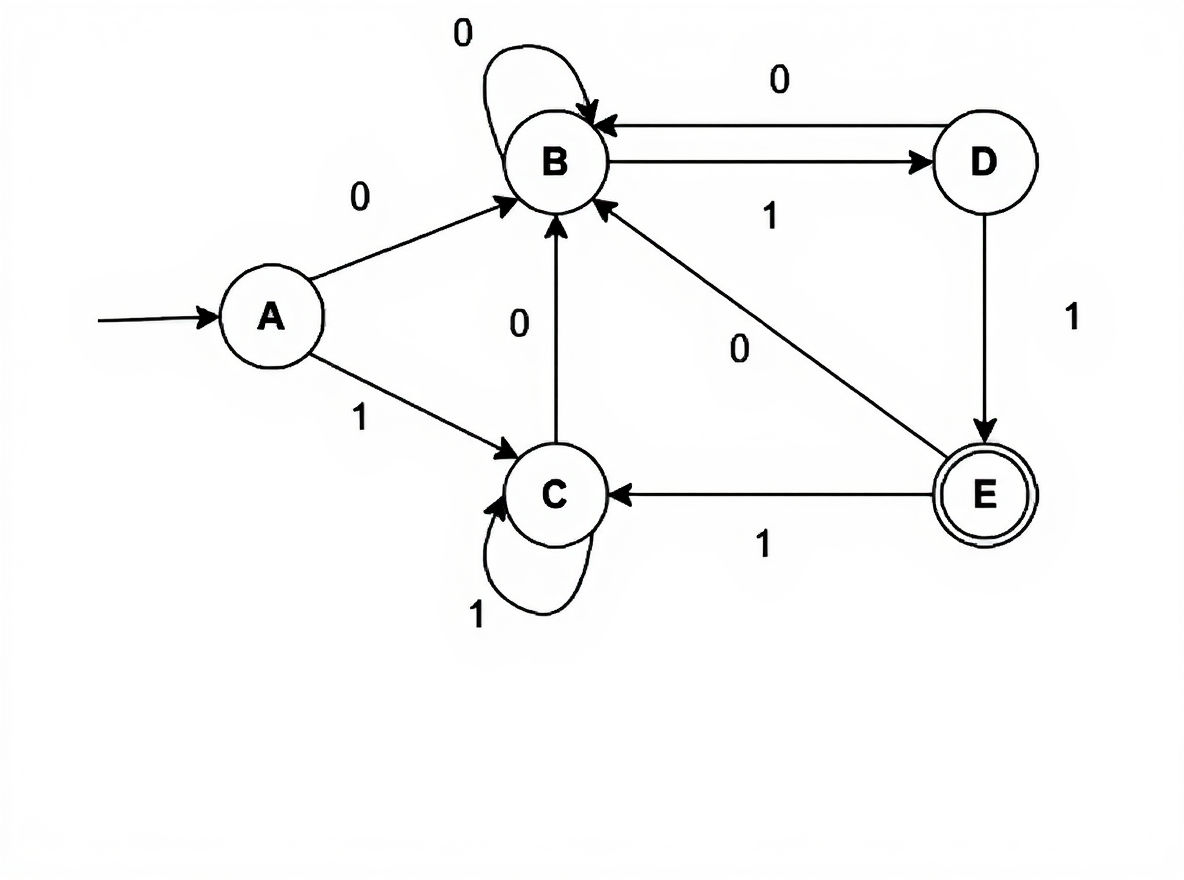 [10]
[10]

2.
Represent the following regular grammar to finite automata.
[5]
Turing Machines
1.
Define Turing machine as enumerators of strings of a language. Encode the Turing machine TM = ({q0, q1, q2}, {a, b}, {a, b, B}, δ, q2, B, F) with input w = ba and δ is defined as follows: δ(q0, b) → (q1, b, R), δ(q1, a) → (q2, a, R), δ(q2, a) → (q1, a, R), δ(q2, b) → (q2, b, L) [10]
2.
For the following Turing Machine, test whether the string “())))” is accepted or rejected and represent it in transition diagram.
[5]
Undecidability and Intractability
1.
What is undecidable problem? Discuss about Post Correspondence Problem. [5]
2.
Differentiate between Class P and Class NP problem. Mention the transition function of DFA, NFA, and ε-NFA. [5]