Semester
Subject
Year
B.Sc Computer Science and Information Technology
Institute of Science and Technology, TU
Discrete Structures (CSC165)
Year Asked: 2076, syllabus wise question
Counting and Discrete Probability
1.
How many 3 digits numbers can be formed from the digits 1,2,3,4 and 5 assuming that:a. Repetitions of digits are allowed b. Repetitions of digits are not allowed [5]
2.
Define ceiling and floor function. Why do we need Inclusion - Exclusion principle? Make it clear with suitable example. [5]
Induction and Recursion
1.
State pigeonhole principle. Solve the recurrence relation , with initial conditions . [10]
2.
Prove that for every positive integer is even integer using mathematical induction. [5]
Integers and Matrices
1.
Find the value of x such that x = 1 (mod 3), x = 1 (mod 4), x = 1 (mod 5) and x = 0 (mod 7) using Chinese remainder theorem. [10]
2.
Define reflexive closure and symmetric closure. Find the remainder when is divided by x + 2 using remainder theorem. [5]
Logic and Proof Methods
1.
All over smart people are stupid. Children of stupid people are naughty. John is a children of Jane. Jane is over smart. Represent these statements in FOPL and prove that John is naughty. [5]
Relations and Graphs
1.
Define Euler circuit with suitable example. Find the maximal flow s to t from the given network flow. 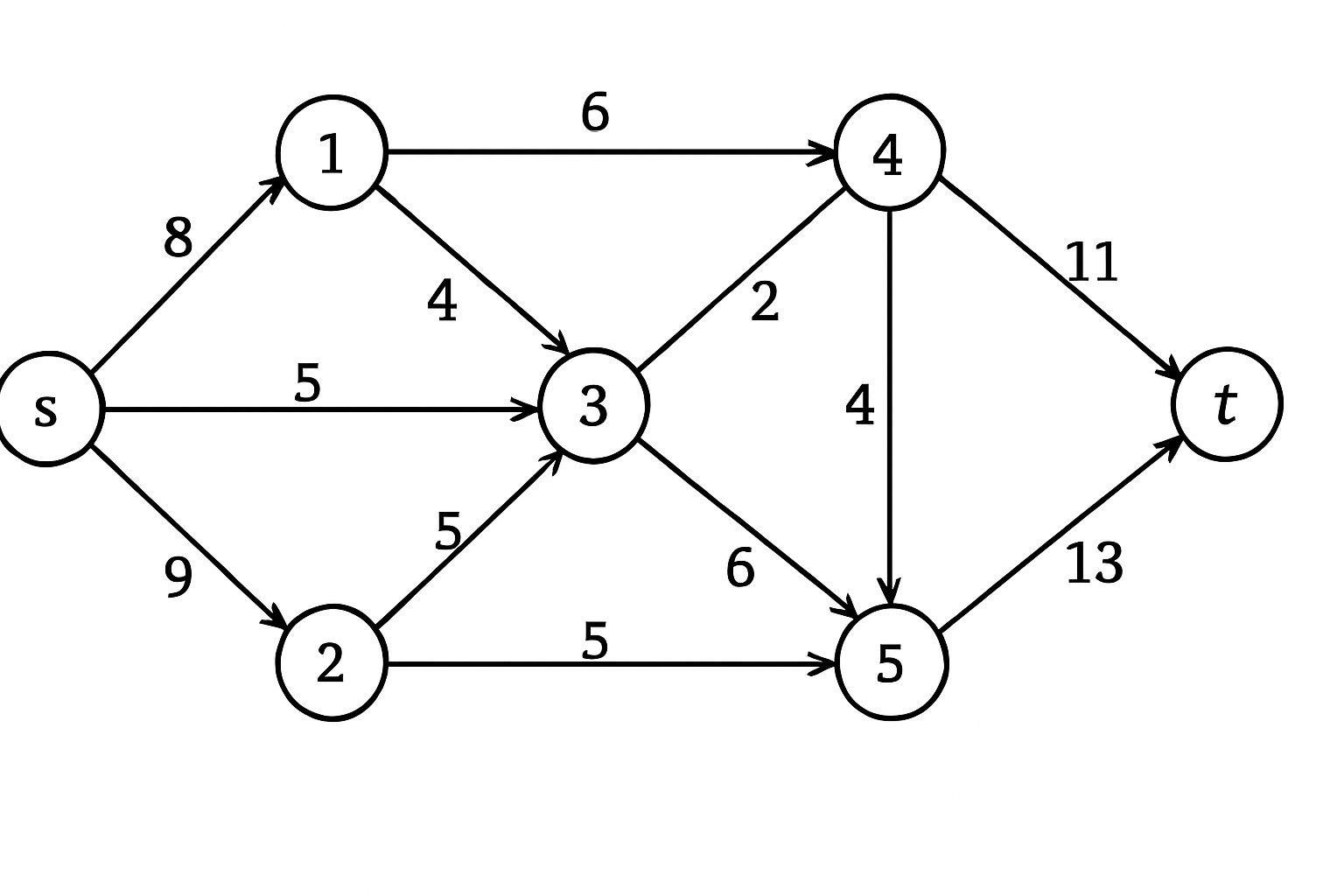 [10]
[10]

2.
Which of the following are possets? [5]
3.
Define Euler path and Hamilton path. Give examples of both Euler and Hamilton path. [5]
4.
What is minimum spanning tree? Explain Kruskal's algorithm for finding minimum spanning tree. [5]
5.
List any two applications of graph coloring theorem. Prove that 'A tree with n vertices has n-1 edges'. [5]