Semester
Subject
Year
B.Sc Computer Science and Information Technology
Institute of Science and Technology, TU
Discrete Structures (CSC165)
Year Asked: 2078, syllabus wise question
Counting and Discrete Probability
1.
What is the coefficient of in ? Describe how relation can be represented using matrix. [5]
2.
Show that if there are 30 students in a class, then at least two have same names that begin with the same letter. Explain the pascal's triangle. [5]
3.
Represent any three set operations using Venn-diagram. Give a recursive defined function to find the factorial of any given positive integer. [5]
Induction and Recursion
1.
Prove that for all integers x and y, if is even then x + y is even. Using induction prove that [10]
2.
Solve the recurrence relation , with initial conditions , . [5]
3.
Prove that if n is positive integer, then n is odd if and only if 5n + 6 is odd. [5]
Integers and Matrices
1.
Define zero-one matrix. Explain the types of function. [5]
Logic and Proof Methods
1.
State division and remainder algorithm. Suppose that the domain of the propositional function P(x) consists of the integer 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4. Write out each of the following propositions using disjunctions, conjunctions and negations. [10]
2.
Define proposition. Consider the argument 'John, a student in this class knows how to write program in C. Everyone who knows how to write program in C can get a high paying job. Therefore, someone in this class can get high paying job'. Now, explain which rules of inferences are used for each step. [5]
Relations and Graphs
1.
List all the necessary conditions for the graph to be isomorphic with an example. Find the maximal flow from the node SOURCE to SINK in the following network flow. 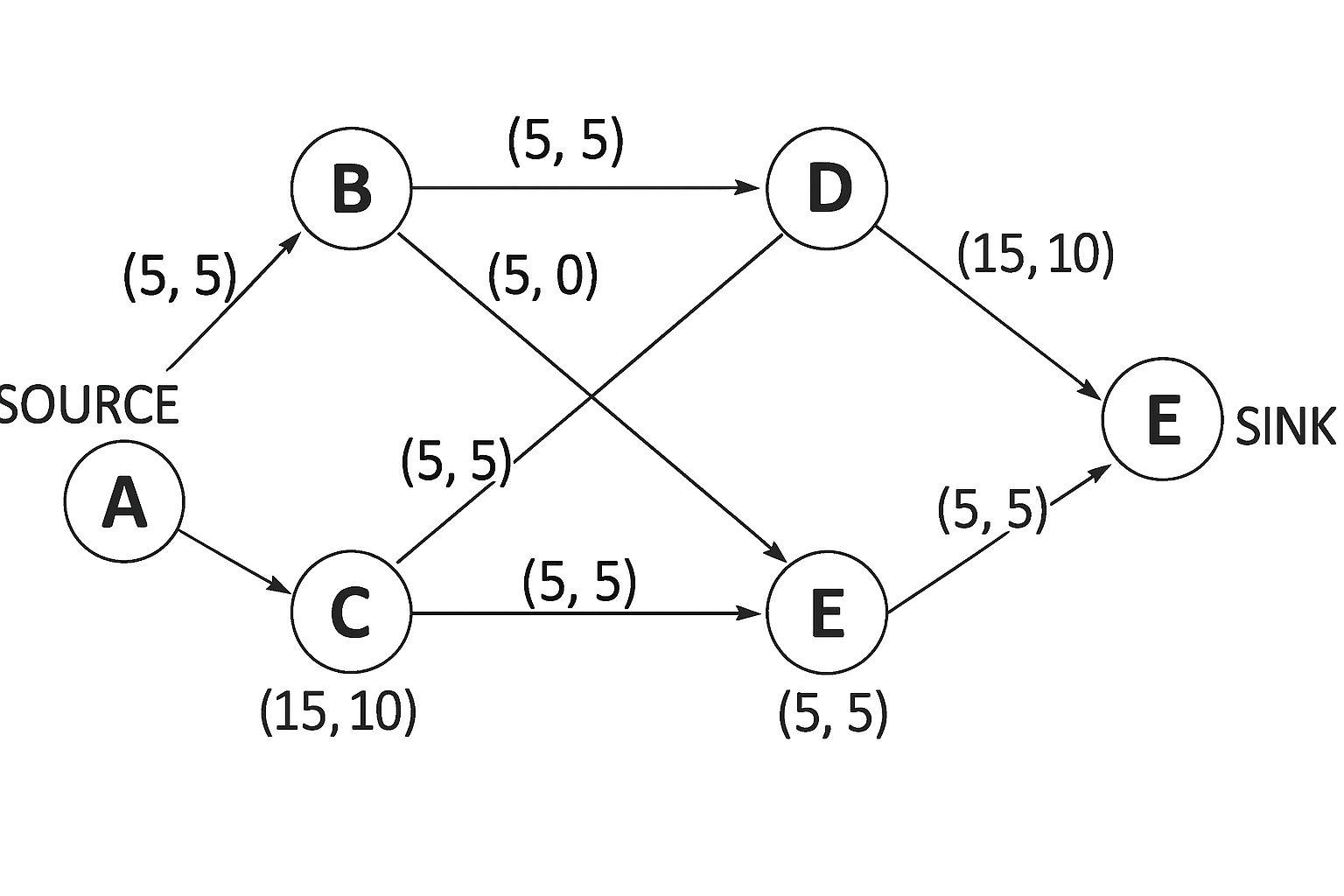 [10]
[10]

2.
Illustrate the Dijkstra's Algorithm to find the shortest path from source node to destination node with an example. [5]
3.
What are the significance of Minimum Spanning Tree? Describe how Kruskal's algorithm can be used to find the MST. [5]